In 2026, email deliverability shifts from being a “technical curiosity” to a revenue protection strategy. Businesses and individuals aiming for higher inbox placement rates will benefit from the following strategies:
- Establishing a positive sender reputation score
- Implementing email authentication protocols
- Practicing email list hygiene
- Conducting automated email warmup
- Complying with global regulations and inbox provider requirements
- Monitoring and tracking important reputation metrics
This guide provides a comprehensive roadmap to navigating the 2026 deliverability landscape. You’ll learn how to build technical foundations that inbox providers trust, maintain the sender reputation that keeps you out of spam, and leverage modern AI-driven tools to optimize the process.
Here’s why deliverability is your most important growth metric
Email deliverability is your most important growth metric because a lot is riding on it. If your emails don’t land in the inbox, they won’t be seen. They won’t be read, they won’t be clicked, and all your efforts will go to waste.
Even as sales teams craft perfect outreach sequences and marketing departments design beautiful campaigns, a silent crisis is unfolding.
Your carefully researched prospects never see your outreach. Your product updates vanish before reaching customers, and your follow-ups are filtered before they can convert.
You’re not just losing emails. You’re losing deals, opportunities, and market share.
Additionally, Email Service Providers (ESPs) like Gmail, Yahoo, and Microsoft are becoming even stricter with their bulk sending requirements such as:
- Spam complaints must be kept below 0.3%
- Strict adherence to SPF/DKIM/DMARC compliance
- Easy unsubscribe function
- Deletion of dormant accounts inactive for a period of time (2 years for Gmail, 12 months for Yahoo)
One misstep (a missing DMARC record, a 0.4% spam complaint rate, or a cold domain that suddenly sends in bulk) can send your entire sender reputation down the drain.
What is email deliverability in 2026?
Email deliverability is defined as the percentage of sent emails that land in the recipient’s primary folder—not the spam folder, not the promotions tab or social tab, and not sent back to the sender.
In 2026, inbox placement is shaped by three critical factors working together:
- Technical authentication: SPF/DKIM/DMARC protocols that prove your legitimacy, credibility, and that your emails haven’t been tampered with in transit
- User behavior signals: How recipients interact with your emails through opens, clicks, replies, and whether they mark your messages as spam
- Strict provider rules: Compliance with evolving requirements from Gmail, Yahoo, Microsoft, and other major inbox providers
Not sure where you stand currently in terms of email deliverability? Try Warmy’s free email deliverability test.
What does the global email landscape look like in 2026?
The email ecosystem is expanding much like the universe. Some essential facts to arm yourself with:
- The number of emails sent and received per day globally is predicted to reach 408.2 billion by 2027.
- Global email usage reached 376.4 billion daily messages in 2025, a 4% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) since 2018. Volume is forecasted to reach 392.5 billion in 2026 and 408.2 billion in 2027.
All of these numbers come together to form a coherent message: the competitive landscape within the email industry is getting tougher.
Understanding sender reputation: what’s the big deal?
Your sender reputation score is essentially your email credit score:
- It is a numerical measure that determines whether your emails are trusted enough to reach the inbox.
- Email Service Providers (ESPs) and inbox providers assign this score based on your sending behavior, and it directly influences where your emails land.
How do sender reputation scores work?
Your sender reputation is translated into a numerical score, typically ranging from 0 to 100.
While the exact algorithms vary by provider, the general framework follows a consistent pattern:
Score range | Reputation status & impact |
Around 90-100 | High reputation. Consistently low spam complaints, strong engagement signals, and proper authentication protocols. Emails reliably reach the primary inbox. |
Around 70-89 | Medium reputation. Minor issues with engagement, occasional bounces, or intermittent spam folder placement. Deliverability is inconsistent. |
Around below 70 | Low reputation. Frequent spam complaints, high bounce rates, or blacklisting. Emails are likely blocked or sent directly to spam folders. |
Key factors influencing your sender reputation
Email Service Providers evaluate your sender reputation by monitoring multiple variables that provide insight into your sending practices and recipient relationships:
- Spam complaint rates: The percentage of recipients who mark your emails as spam. This is one of the most damaging metrics to your reputation. In 2026, you must stay below 0.3%, with best-in-class senders targeting 0.1% or lower.
- Bounce rates: The percentage of emails that fail to deliver. High bounce rates (above 2%) signal poor list management practices, purchased lists, or outdated data. These are all reputation killers.
- Engagement metrics: Opens, clicks, and replies demonstrate that recipients want your emails. Low engagement suggests your content isn’t relevant or welcome, which inbox providers may interpret as a spam signal.
- Spam trap hits: Sending to spam traps (fake email addresses created specifically to catch spammers) severely damages your reputation. These addresses usually appear in purchased lists or outdated databases, which tells ESPs you don’t maintain a clean list or you don’t take the time to validate your recipients’ contact details.
- Sending patterns: Steady, consistent email volume without sudden spikes signals a predictable, trustworthy sender. Erratic sending patterns trigger spam filters.
Why does sender reputation directly impact revenue?
- Poor sender reputation means reduced deliverability. This creates a negative feedback loop. When ESPs distrust your domain, the likelihood of your future emails landing in spam will increase.
- Reduced deliverability leads to lower engagement rates. When more emails land in spam, recipients can’t open them or engage with them. This further lowers engagement metrics and reputation score.
- The marketing budget is wasted. You’ve invested in email platforms, copywriters, designers, and list building. When emails don’t reach the inbox, poor sender reputation equals burning through your marketing budget.
Technical foundations for email deliverability: Authentication is no longer optional
In 2026, email authentication protocols are not advanced technical configurations. They are baseline requirements for inbox placement. Even legitimate businesses risk being flagged as spam without proper authentication.
Email authentication serves two critical functions:
- It proves to inbox providers that you are who you claim to be
- It ensures your messages haven’t been tampered with during transit.
Without these protocols in place, your domain is vulnerable to impersonation, and your emails will be treated with suspicion.
The three mandatory authentication protocols
1. SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
- SPF specifies which mail servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of your domain.
- When an email arrives, the receiving server checks the sender’s IP address against the SPF record in your domain’s DNS settings.
- If the IP isn’t on the approved list, the email fails SPF authentication.
Why SPF matters: It prevents malicious actors from spoofing your domain to send phishing emails or spam. Without SPF, anyone can claim to send email from your domain.
Implement your SPF record properly. Use Warmy’s Free SPF Record Generator.
2. DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
- DKIM adds a digital signature to your emails.
- The recipient’s server validates this against a public key stored in your DNS records.
- This signature proves the email content hasn’t been altered during transmission.
Why DKIM matters: It ensures message integrity and builds trust with inbox providers. DKIM also helps protect your reputation even when emails are forwarded, because the signature travels with the message.
3. DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance)
- DMARC works alongside SPF and DKIM to tell inbox providers how to handle emails that fail authentication checks.
- Your DMARC policy can instruct providers to quarantine, reject, or monitor suspicious emails.
- DMARC also provides reports showing who is sending email from your domain.
Why DMARC matters: It gives you control over email authentication enforcement and visibility into unauthorized use of your domain. Gmail and Yahoo require DMARC for bulk senders as of 2024, making it non-negotiable in 2026.
Do away with second-guessing your DMARC records. Try Warmy’s free DMARC Record Generator here.
Optional: BIMI (Brand Indicators for Message Identification)
- BIMI is an optional but powerful addition that displays your brand logo next to your emails in supported inbox providers.
- It requires DMARC enforcement at the ‘quarantine’ or ‘reject’ level and a verified mark certificate.
Why BIMI matters: It provides instant visual brand recognition in crowded inboxes, increasing trust and open rates. While not required, implementing BIMI signals to inbox providers that you take email authentication seriously.
Authentication protocol comparison
Protocol | Primary function | 2026 Status |
SPF | Authorizes which servers can send email from your domain | Mandatory for all bulk senders |
DKIM | Verifies email content integrity with digital signatures | Mandatory for all bulk senders |
DMARC | Enforces authentication policies and provides reporting | Mandatory for Gmail, Yahoo, Microsoft bulk senders |
BIMI | Displays brand logo in inbox for visual authentication | Optional but recommended for brand recognition |
Email list hygiene: An overlooked revenue driver
List hygiene is the practice of regularly cleaning and maintaining your email contact database to remove inactive, invalid, or problematic addresses.
For high-volume senders, it’s a tedious process to manually skim through email lists before every big campaign. Yet, maintaining list hygiene is one of the most impactful actions you can take for deliverability.
What is a “dirty” email list?
- It is filled with outdated addresses, typos, spam traps, and unengaged contacts
- This creates multiple problems like higher bounce rates which can damage your reputation and low engagement signals which tell inbox providers that your emails aren’t wanted
- These lists can sometimes trigger permanent SMTP Errors like Error 510.
How does email list hygiene benefit email deliverability?
- Fewer bounces protect your reputation. When you remove invalid addresses, your bounce rate drops below the critical 2% threshold, signaling to inbox providers that you maintain quality data.
- Higher engagement improves deliverability. Targeting engaged subscribers helps increase your open and click rates, which inbox providers interpret as a strong positive signal.
- Better ROI from email marketing. Clean lists mean your messages reach people who actually want them, leading to higher conversion rates and more revenue per email sent.
- Reduced sending costs. Many email platforms charge based on list size or email volume. Removing inactive contacts directly reduces your platform costs.
Best practices for email list hygiene
- Use double opt-in for all new subscribers. This ensures only valid, engaged email addresses enter your database. It prevents typos, reduces spam complaints, and builds a foundation of permission-based marketing.
- Remove hard bounces immediately. Email addresses that permanently fail delivery should be removed from your list right away. Repeatedly experiencing hard bounces signals poor list management.
- Regularly sunset inactive subscribers. If a contact hasn’t opened or clicked any email in 6-12 months, they may be dragging down your engagement metrics.
- Make unsubscribing easy. A clear, one-click unsubscribe option may seem counterintuitive, but it prevents spam complaints. Plus, Gmail now requires this.
- Segment by engagement level. Divide your list based on how actively contacts engage with your emails. This allows you to send targeted campaigns to your most responsive subscribers while testing re-engagement strategies on less active segments.
- Use a trusted Email Validation tool. Warmy also provides 10,000 free credits with any plan, so users can import their contact lists and let Warmy identify the invalid ones.

How has the AI revolution affected email warmup?
Email warmup is yet another unsung hero of the email deliverability game. Without it, even if your authentication protocols are set up properly and even if your lists are clean, deliverability rates can still drop.
What is email warmup?
- Domain and IP warming is the process of gradually building sender reputation with inbox providers by slowly increasing email volume over time.
- When you send from a new domain or IP address, inbox providers have no sending history to evaluate so they don’t trust you yet.
- Attempting to send high volumes right away immediately raises red flags and damages your reputation before you’ve even started.
In 2026, manual warmup processes are now being replaced by AI-driven email warmup that simulates natural human email behavior.
How does AI-powered warmup work?
Manual warm-up processes require constant monitoring, precise volume calculations, and human judgment about when to scale up or pause.
AI-driven warm-up tools like Warmy.io analyze thousands of data points per domain, adjusting strategies in real-time based on inbox placement tests, spam folder detection, and engagement metrics.
This level of optimization is impossible to achieve manually. AI-driven warm-up systems operate by creating authentic email interactions that demonstrate to inbox providers that your domain sends valuable, wanted communications.
Choosing the right partner for deliverability: Why Warmy is the premium choice
The deliverability tools market includes options like Lemwarm, Mailwarm, Folderly, and Warmbox. So if you find yourself asking why Warmy is the top email deliverability provider, here are the reasons:
Stronger deliverability with AI-driven tools
Warmy is the premium, highest-quality deliverability solution built specifically to help emails land in inboxes. With the ability to send a maximum of 5,000 warmup emails a day, Warmy is the most robust of all warmup tools.
Unlike basic tools that only send emails back and forth, Warmy uses its proprietary AI, Adeline, to simulate authentic human behavior, dynamically adjust warmup strategies based on your domain’s unique signals, and provide comprehensive monitoring and analysis that prevents problems before they impact revenue.
AI-powered domain warming

Warmy’s email warmup feature builds sender reputation by going beyond simple warmup. In fact, the warmup process itself can be optimized further:
- Adjusts sending pace dynamically based on your domain’s specific engagement metrics and reputation signals, accelerating when performance is strong and slowing when issues are detected.
- Generates email warmups in 30+ languages, ensuring warmup traffic appears authentic even for global sending patterns.
- Utilizes advanced seed lists with genuine email addresses across all major providers (Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo, and private SMTP servers) that engage with your emails like real recipients.
- Customizes engagement patterns for B2B or B2C sending based on your target audience, optimizing the warm-up process for your specific use case.
- Provides options to customize even the warmup topic so your warmup can be as close to your target audience as possible
- Provides an option to customize warmup distribution across multiple providers.
Comprehensive domain health monitoring
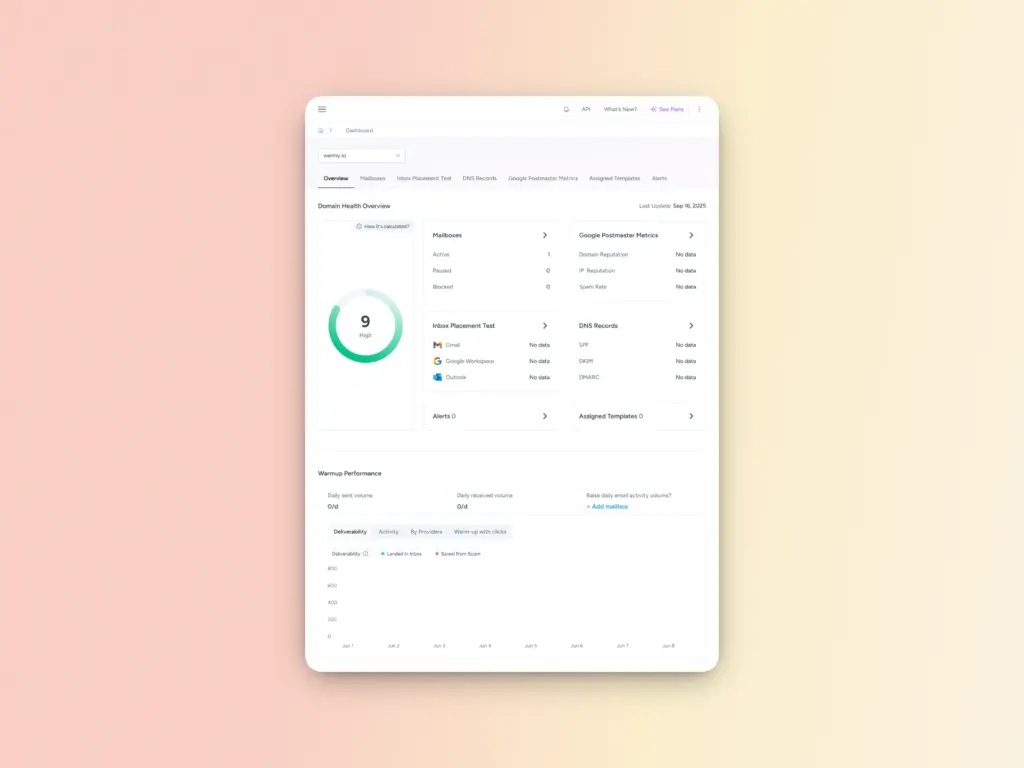
Warmy’s Domain Health Hub consolidates all critical deliverability metrics into a single dashboard, providing:
- A numeric health score based on inbox placement tests, DNS authentication status, and Google Postmaster data.
- Real-time monitoring of spam rate trends, inbox placement percentages, and overall deliverability performance with weekly or monthly tracking.
- Comprehensive DNS health checks that validate SPF, DKIM, DMARC, rDNS, MX, and A records, alerting you to authentication issues before they impact deliverability.
- Provider-specific insights showing your reputation and inbox placement rates across Gmail, Microsoft, Yahoo, and other major providers.
Template checker for anti-spam content optimization

Even with perfect technical configuration and a warmed domain, content issues can still trigger spam filters. Warmy’s Template Checker analyzes your email messages before sending to ensure they comply with deliverability best practices by:
- Scanning for spam trigger words and phrases that commonly cause emails to be filtered.
- Evaluating subject line length, personalization quality, and formatting for optimal inbox placement.
- Providing a deliverability score with specific recommendations for improving content before you hit send.
- Offering a Chrome Extension that integrates directly into your email platform for real-time assessment and adjustments.
Conclusion: 5 takeaways for email success in 2026
Email deliverability in 2026 is a technical discipline, a behavioral science, and a revenue protection strategy. Success requires understanding inbox provider algorithms, implementing proper technical foundations, and maintaining vigilant monitoring of reputation signals.
Here are the five critical takeaways that separate high-performing senders from those watching their emails vanish into spam folders:
- Reputation beats content. The most brilliant copy, the most compelling offer, the most perfect design don’t matter if your sender reputation is damaged.
- Authentication is the baseline. SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are baseline requirements. You cannot compete for inbox space without proper email authentication in 2026.
- Clean your lists religiously. A small, engaged list will always outperform a large database filled with inactive contacts, typos, and spam traps.
- Monitor proactively, not reactively. Fixing a damaged reputation is harder than preventing problems. Regular monitoring of spam rates, bounce rates, and blacklist status allows you to address issues before they cause serious damage.
- Automate your growth. The complexity of modern deliverability requirements makes manual processes obsolete. AI-driven tools handle domain warming, reputation monitoring, and content optimization with precision that humans can’t match.
Email remains the highest-ROI marketing channel when done correctly. The senders who treat it as the revenue protection strategy it is will continue reaching inboxes and converting prospects while their competitors watch emails disappear.
The 2026 deliverability landscape may be unforgiving at times, but the rewards for those who master it are substantial. Take control of your email deliverability today. Start your automated warmup and experience the difference.
FAQ
What is a good inbox placement rate?
The industry average inbox placement rate is approximately 83.5%, meaning that about 83.5% of emails successfully reach recipients’ primary inboxes rather than spam folders or other filtered locations. However, high-performing senders consistently achieve 90% or higher inbox placement rates. Your target should be 90%+ if you want to remain competitive in 2026. Anything below 80% indicates serious deliverability problems that require immediate attention.
How do I avoid the spam folder?
Avoiding spam folders requires a combination of technical authentication, reputation management, and content optimization. First, ensure proper SPF, DKIM, and DMARC authentication is configured correctly. Second, maintain your spam complaint rate below 0.3% (targeting 0.1%). Third, use AI-driven automated warm-up to build sender reputation before sending at scale. Fourth, practice rigorous list hygiene by removing bounces, sunset inactive subscribers, and never purchase email lists. Finally, monitor your domain health continuously to catch and fix issues before they cause spam folder placement.
Is manual warm-up still effective in 2026?
No, manual warmup processes are no longer competitive in 2026. Modern inbox provider algorithms are sophisticated enough to detect artificial patterns and simple volume ramping. AI-driven automation has become the standard because it can simulate authentic human behavior patterns, adjust dynamically based on real-time reputation signals, and operate across multiple providers and languages simultaneously. Manual processes require constant oversight, can’t match the behavioral sophistication of AI systems, and are prone to human error in timing and volume decisions.
What is a ‘good’ spam complaint rate?
In 2026, you must stay below 0.3% spam complaint rate to maintain good standing with Gmail, Yahoo, and other major providers. However, best-in-class senders target 0.1% or lower. A spam complaint rate above 0.5% will cause immediate deliverability problems, including spam folder placement and potential blocking. Even temporary spikes above the 0.3% threshold can damage your sender reputation in ways that take months to repair.
What happens if I don’t set up DMARC?
Without DMARC implementation, legitimate businesses risk being filtered as spam or blocked entirely by Gmail, Yahoo, and Microsoft—the three providers that collectively control the vast majority of email inboxes globally. DMARC is now mandatory for bulk senders (those sending more than 5,000 emails per day) to these providers. Even if you’re not technically required to have DMARC, lacking it signals to inbox providers that you don’t take email authentication seriously, which can harm your deliverability. Additionally, without DMARC, you have no visibility into who is sending email from your domain, leaving you vulnerable to brand impersonation and phishing attacks.
How often should I clean my email list?
Email list cleaning should be a continuous process, not a one-time event. At minimum, you should remove hard bounces immediately after each campaign, sunset inactive subscribers every 6-12 months, and conduct comprehensive list hygiene audits quarterly. High-volume senders should implement automated list cleaning processes that run weekly or even daily to catch and remove problematic addresses before they damage reputation.







![Text that reads: SMTP Error 535 5.7.0 How to Fix It [SOLVED] on a white background, featuring a faint orange-pink gradient on the right side and highlighting the smtp error 535 5.7.0 issue.](https://warmy-blog-wordpress-bucket.s3.amazonaws.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/13051103/535-5.7.0.webp)

![Text graphic featuring the message: smtp error 553 5.7.2 How to Fix It [SOLVED] in bold black and red on a white and orange gradient background.](https://warmy-blog-wordpress-bucket.s3.amazonaws.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/11153221/SMTP-553-5.7.2.webp)



